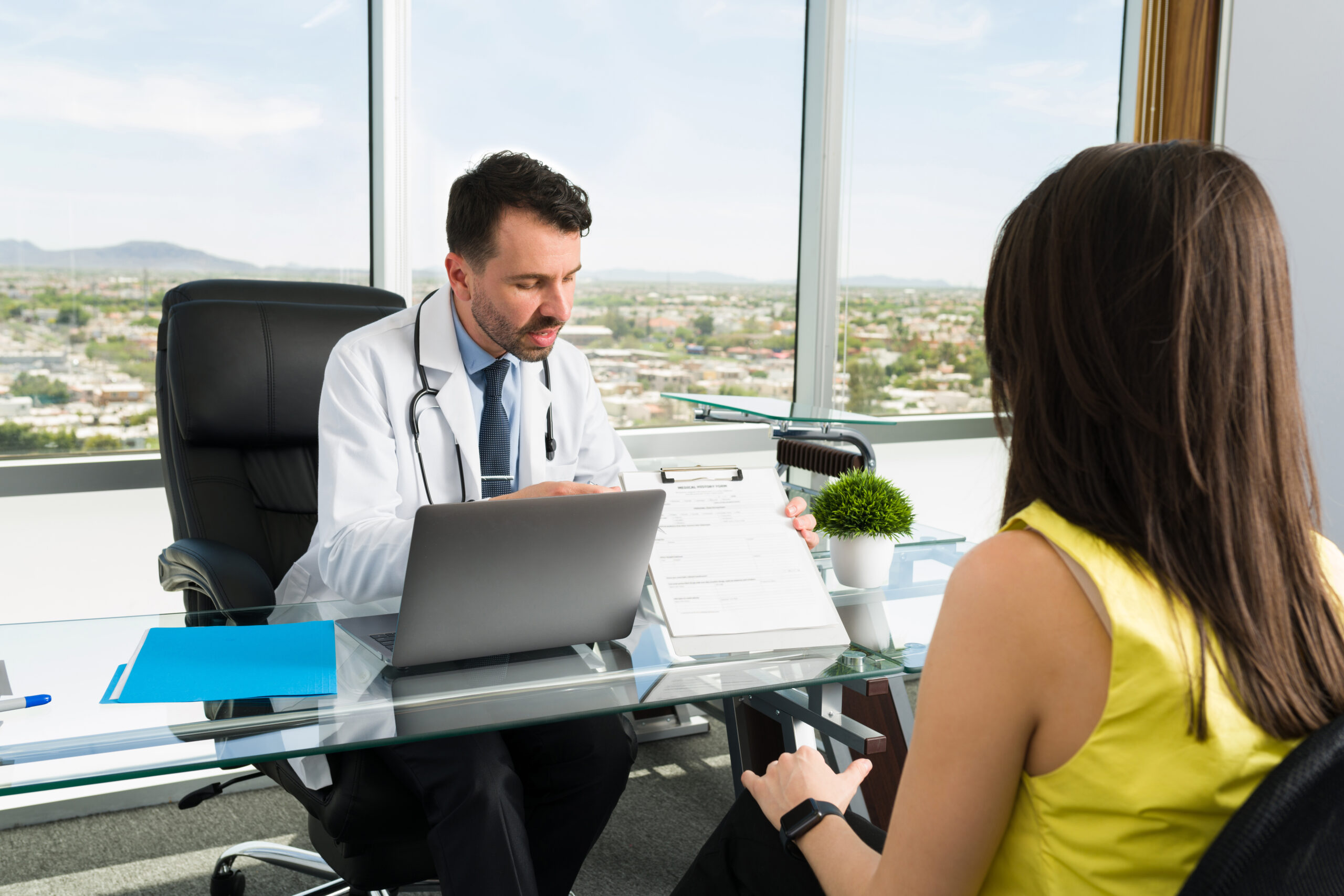
When considering a move to Tennessee, one of the most important aspects to evaluate is the health care system. From access to affordability, Tennessee’s health care landscape has its own unique characteristics that can significantly impact your quality of life. Whether you’re relocating, retiring, or just planning for the future, this guide offers a complete look at what to expect from health care in the Volunteer State.
Overview of Health Care in Tennessee
Tennessee has a mixed health care system, blending public health programs with a broad private care network. The state is home to some nationally recognized hospitals and a growing number of urgent care clinics and telehealth options. While health care in major cities like Nashville and Memphis is widely accessible, rural areas face more limited resources.
Access to Health Care in Tennessee
Urban vs. Rural Access
-
Urban areas (e.g., Nashville, Knoxville, Chattanooga) boast high-quality hospitals, clinics, and specialty care centers.
-
Rural regions often struggle with hospital closures, limited specialists, and longer travel times for routine care.
Availability of Providers
-
Primary Care Physicians (PCPs): Tennessee ranks slightly below the national average in PCP availability per capita.
-
Telehealth Access: Post-pandemic expansion has made telemedicine services more common, especially in rural counties.
Quality of Health Care in Tennessee
Hospital Ratings
Tennessee is home to several highly rated hospitals:
-
Vanderbilt University Medical Center (Nashville): Renowned for specialty care and research.
-
St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital (Memphis): Internationally acclaimed for pediatric oncology.
-
Erlanger Health System (Chattanooga): Recognized for cardiovascular and stroke care.
Public Health Performance
While Tennessee has made strides in health system quality, challenges remain in areas like:
-
Obesity and chronic illness rates
-
Smoking prevalence
-
Rural maternal care access
Cost of Health Care in Tennessee
Health Insurance Options
Tennessee offers a range of options through:
-
Employer-sponsored plans
-
ACA Marketplace (Healthcare.gov)
-
TennCare (Medicaid) for qualifying low-income residents
-
Medicare for seniors and eligible disabled residents
Average Monthly Premiums (2025 Estimates)
| Plan Type | Avg. Monthly Premium |
|---|---|
| Individual Plan | $450 – $600 |
| Family Plan | $1,200 – $1,800 |
| ACA Bronze Tier | $380 – $450 |
| ACA Silver Tier | $470 – $580 |
Premiums vary based on age, location, and subsidies.
Out-of-Pocket Costs
-
Primary care visit: $110 – $180 (without insurance)
-
Emergency room visit: $1,200 – $2,000
-
Prescription drug prices: Generally average, but savings programs and discount cards are widely used
Health Care for Seniors and Retirees
Tennessee is increasingly popular among retirees due to:
-
No state income tax on retirement income
-
Access to Medicare Advantage plans
-
Geriatric services in top hospitals
-
Affordable long-term care relative to national averages
Tip: Seniors in rural areas should verify local care options before relocating.
Health Challenges in Tennessee
Despite improvements, Tennessee faces several ongoing health challenges:
-
High rates of diabetes and heart disease
-
Opioid addiction crisis, especially in eastern counties
-
Limited mental health services in smaller towns
State and private programs are addressing these issues through telemedicine expansion, addiction recovery support, and rural health incentives.
Resources for Health Care in Tennessee
-
Tennessee Department of Health – Public health programs and statistics
-
Healthcare.gov – ACA health plans for Tennessee
-
TennCare – Tennessee’s Medicaid program
-
Medicare.gov – Coverage for seniors
-
Local community health centers – Often offer sliding scale services
Final Thoughts
Tennessee’s health care system provides solid options for those living in urban and suburban areas, with growing support for rural communities. If you’re moving to the state, it’s wise to research the health care providers and insurance plans in your specific region. While there are some challenges, especially in rural access and chronic illness rates, the state is making measurable progress in improving care for all residents.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Is health care in Tennessee affordable?
Tennessee has relatively moderate health care costs compared to other states. Costs are lower in rural areas but access may be limited. Health insurance premiums are in line with national averages.
Does Tennessee have good hospitals?
Yes, especially in cities like Nashville, Memphis, and Knoxville. Vanderbilt and St. Jude are nationally ranked institutions.
Is Tennessee a good state for health care in retirement?
Yes, particularly due to no state income tax, Medicare Advantage options, and a lower cost of long-term care.
What is TennCare?
TennCare is Tennessee’s Medicaid program, offering coverage to eligible low-income individuals, families, children, pregnant women, and people with disabilities.
Can I use telemedicine in Tennessee?
Yes, telehealth is widely available and encouraged in both rural and urban areas, with support from state health initiatives.